
Table of Contents [hide]
The beam angle is the angle between the centerline of the beam and the point where the light intensity decreases to 50% of the maximum light intensity on the centerline. The beam angle describes how the light source's beam radiates outward from the beam centerline.
The LED light-emitting angle is also called the power angle. Usually, we use the half-power angle, which is the angle at 50% of the light-emitting intensity. Of course, some people use 60%, 80%, or even 90%, depending on the application.
The beam angle is reflected in the same floor height, and the spot size and light intensity on the illuminated wall are different. The selection of different beam angles has a great impact on the creation of the environmental atmosphere.
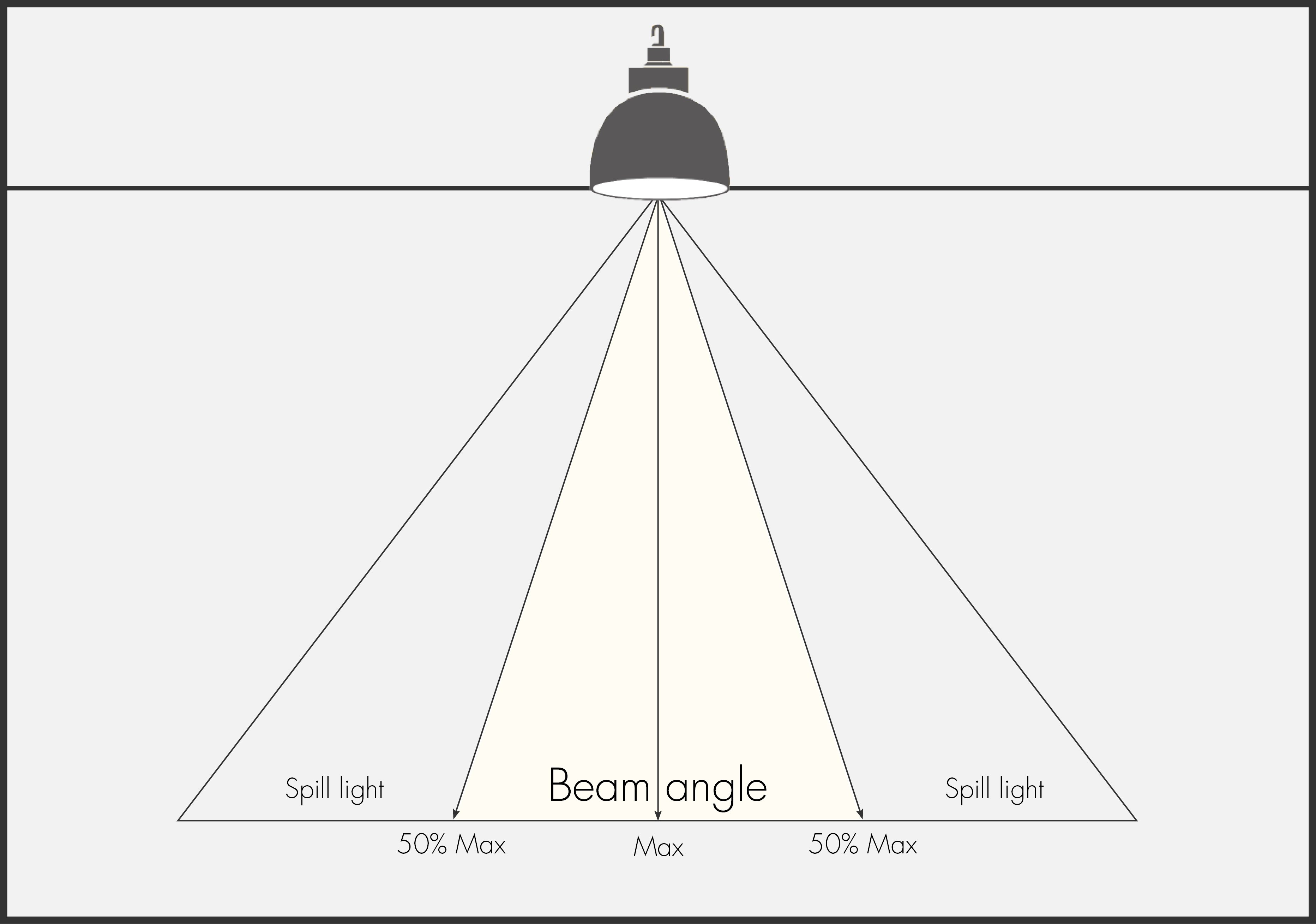
Generally speaking, the smaller the beam angle, the sharper and colder the light effect, on the contrary, the larger the beam angle, the softer the light.
Narrow beam: beam angle <20 degrees; mainly for key lighting, highlighting gorgeous light;
Medium beam: beam angle 20~40 degrees;
Wide beam: beam angle > 40 degrees, wall washing or local lighting, highlighting the light level, light and dark contrast.
Choose lamps with a wide beam angle, so that the entire space has a wider range of light and a softer atmosphere;
Narrow beam angle lamps are selected to highlight the central object, forming a strong contrast of light and darkness between the surroundings and the center, making the overall atmosphere stronger. The overall atmosphere is quite strong.
The angle of the beam determines the distribution of the light. The wide beam angle produces softer light and spreads better in different areas of the room. The narrow beam angle produces concentrated light that can be used for accent lighting. This makes the light more intense and concentrated. The LED lights are available in various beam angles: from 15° to 120°. Choose the appropriate beam angle to improve lighting in high-rise applications. With LEDs, you don't need a reflector to collect it and direct it to the floor, such as high halide metal halide light fixtures.
Choosing the right LED light beam angle is very important for any lighting project. Imagine walking into a dimly lit building, how do you feel about it? You may never want to go there again! One reason this happens is that the light beam angle is wrong. Today, LED will share with you how to choose the right beam angle for LED high bay lights.
The beam angle is the angle at which the LED light spreads on the floor when it is turned on. It can also be called beam spread. Choosing the right type of beam angle can give your building the right ambiance and visibility. The image below shows what the beam angle looks like, it is the beam angle of ZGSM Halo series high bay light.
When choosing the beam angle of the LED high bay light, the basic consideration is to ensure that the space you want to light can be illuminated. In fact, for any lighting purpose, we need to consider a few factors.
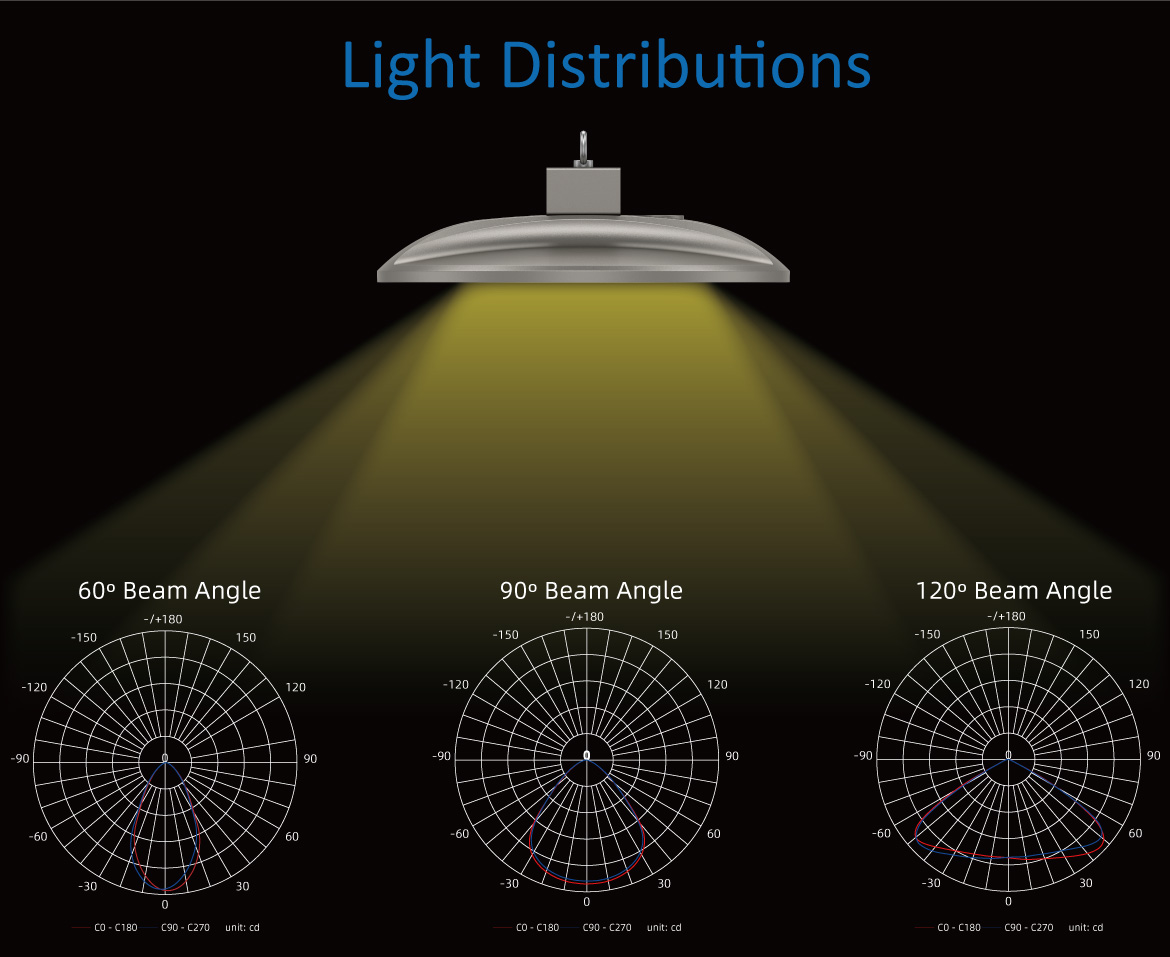
The type of building is one of the factors that determine which LED light beam angle to choose. Because you need to consider how much lighting you need in your building. Then you can choose the correct beam angle. Because depending on the height of the ceiling, the beam angle affects lighting and visibility. For example, warehouses with high ceilings require LED high bay lights with different beam angles than retail stores.
If you have a 50,000 square foot building, how many lumens will provide the right amount of light? According to industry standards, for a commercial space, we need 70 lumens per square foot. As a lighting designer, for any lighting project, you need to make sure you have a lighting layout design before choosing the beam angle of your LED high bay.
After that, now you can calculate how many fixtures you need.
Start by multiplying the square footage of the building by the industry standard to get the total lumens.
50,000 (L x W) x 70 lumens = 3,500,000 lumens (total lumens)
Then multiply the total lumens by the constant 1.40. This number is calculated by adding together the light loss factor (.75) and the utilization factor (.65). You need to take this into account when calculating total lumens for a specific space.
1.40 x 3,500,000 (total lumens) = 4,900,000 lumens (lumen loss)
After Z, you need to add the total lumens and extra lumens together. This will show you the total amount of lumens needed to illuminate the lighting space.
3,500,000 (total lumens) + 4,900,000 (lumen loss) = 8,400,000 lumens
Check the ceiling height to make sure the beam angles overlap. If not, you may end up with a dark, dim area in the building. The overlapping beam angles will ensure the light completely covers your space and prevent injury.
Standard ceiling heights are approximately 7.9 to 8.9 feet. Therefore, a larger beam angle (60 degrees or more) should suffice. If your ceiling height is more than 8.9 feet, you will need a narrow beam angle of fewer than 45 degrees.
In any lighting situation, you will need to adapt to the height of the ceiling to ensure you have a bright workspace. When you use LED high bay lights in industrial areas, you can use high bay lights with reflectors, which can better spread the light.
Depending on the application, you need to choose different types of LED bulbs. In industrial spaces with high ceilings, the higher the fixture, the narrower the beam angle you need. For lower ceilings, the beam angle will be wider. If you are using a LED high bay light with a 360 beam angle, you may consider using a reflector to reflect the light.
To sum up, let's take a look at the application of different lenses and other product features of LED high bay lights.
![]() Installation Manual_HighBayLight_Helios.pdf
Installation Manual_HighBayLight_Helios.pdf
![]() Data Sheet_ HighBayLight_Helios.pdf
Data Sheet_ HighBayLight_Helios.pdf
· LED flood light: 120°-150°
· LED spotlight: 15°-90°
· LED downlight: 120°-160°
· LED high bay light: 60°-120°
· LED corn light: 180°-360°
· LED downlight: 30°-60°
 |  | |
| LED factory lighting project in Canada | ||
 |  |  |
| Garage lighting project in Spain | UFO light project in Lebanon |
A beam angle is an angular expression that shows how light is emitted from a light source. A light source can be defined as a narrow angle of 5 to 45 degrees and a wide angle of 45 to 120 degrees. When no optical material is used, LEDs typically emit light at a 120-degree angle. However, for some types of LEDs, such as TH LEDs, and Power LEDs, an optical material called primary optics can be placed on the LED package. As a result, the LED package can automatically have a 30-degree, 60-degree, or 90-degree light emission angle.
To choose the correct beam angle, you must consider the distance between the fixture and the subject. You must also consider the size of the subject area. Professionals also consider lamp wattage (lumens) as well as foot candles. In general, if you're not sure which beam angle to choose, anything between 60 and 120 degrees will work fine in most cases. If you choose a light with a wide beam angle (about 60 degrees), it's called floodlighting.
Share the Post
Add: 1188 Jinxi South Rd., Linglong Industrial Zone, Lin’An - 311301, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Copyright © Hangzhou ZGSM Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved
